Future of Renewable Energy: “dolar australiano para real” Global Insights 2025
The global energy landscape is undergoing a fundamental transformation, driven by the urgent need to combat climate change and transition to clean, sustainable sources. The future of renewable energy, particularly in the context of economic and geopolitical shifts, is one of the most defining themes of our time. This article explores the key technological innovations, policy decisions, investment trends, and environmental impacts that will shape renewable energy through 2030 and beyond.
Global Innovations in Renewable Technology
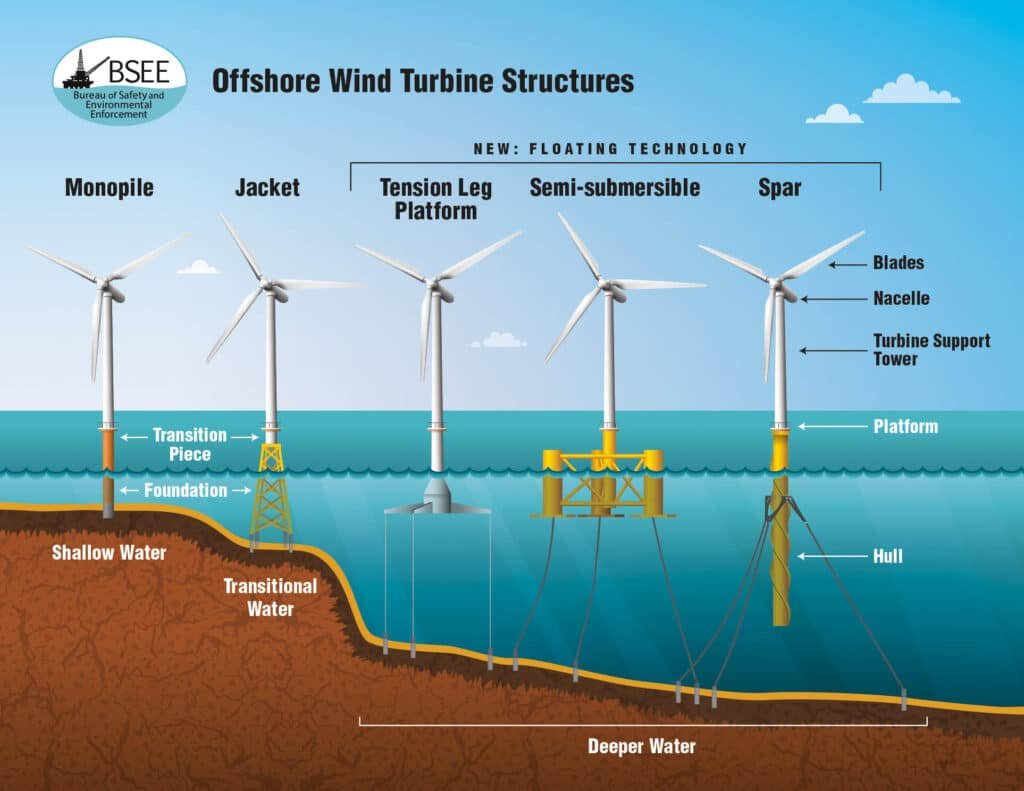
Renewable energy technologies have evolved rapidly. Solar, wind, hydro, and bioenergy are not only more efficient but increasingly accessible. In 2025, solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind technologies are leading the charge. Floating offshore wind turbines now allow energy generation in deeper waters with higher wind consistency. Innovations in solar panels, especially perovskite-based and bifacial models, are pushing energy efficiency above 25% while reducing costs.
In hydropower, smaller-scale run-of-river systems and tidal turbines are emerging as cleaner alternatives to traditional dams. These systems cause less disruption to local ecosystems while still generating substantial power. Bioenergy is also seeing progress, especially with waste-to-energy systems and second-generation biofuels that rely on non-food biomass.
Meanwhile, enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) are expanding the feasibility of geothermal energy in regions previously considered unsuitable. EGS technology allows engineers to create artificial reservoirs in hot rock formations, unlocking vast potential for continuous baseload renewable power.
Government Policies Driving Change

Government policies are critical in accelerating this transition. In the United States, the Inflation Reduction Act has unlocked billions in clean energy tax credits. This policy is a cornerstone of the country’s goal to decarbonize the power sector by 2035. The European Union continues to lead with the European Green Deal and Renewable Energy Directive, both of which set ambitious targets and offer support mechanisms for clean energy deployment.
Australia has invested heavily in utility-scale solar and wind farms, backed by both federal and state incentives. Meanwhile, Asian powerhouses like China and India are scaling up renewables at record pace. China alone accounted for nearly half of all new global solar capacity in 2024. India’s International Solar Alliance and aggressive renewable auctions demonstrate its commitment to energy transition.
Economic Impacts of Renewables
The economic implications are profound. Global investment in clean energy is expected to hit USD 2.2 trillion in 2025, double the projected investment in fossil fuels. This redirection of capital signals growing confidence in renewables as reliable, long-term infrastructure assets.
Job creation is another major benefit. Solar and wind sectors are already significant employers. As energy systems modernize, new jobs are emerging in grid technology, energy storage, and electric mobility. These shifts are critical for economies looking to rebound sustainably after global disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Environmental Benefits
Environmentally, the advantages are clear. Renewable energy drastically reduces greenhouse gas emissions. By replacing fossil fuels with renewables, countries not only meet climate targets but also enjoy improved air quality, reduced water usage, and greater energy independence.
Real-World Examples
Global examples provide context and inspiration. In Denmark, over 50% of electricity now comes from wind power. Morocco’s Noor Solar Complex is one of the world’s largest concentrated solar power projects. In Brazil, bioenergy plays a major role in electricity generation, especially from sugarcane biomass.
Future Predictions and Trends to 2030 and Beyond
Looking ahead to 2030 and beyond, several trends are likely to shape the future of renewable energy. Smart grids and AI-enabled energy management will improve reliability and reduce waste. Battery storage and hydrogen fuel cells will resolve intermittency issues. Floating solar farms and integrated renewable-hybrid systems will expand the geographic footprint of clean energy.
Hydrogen, particularly green hydrogen produced using renewable power, is emerging as a key enabler for decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors such as steel, cement, and long-distance transport. Enhanced geothermal and advanced nuclear may play supporting roles in delivering consistent, non-intermittent power.
Investment and Market Outlook
From an investment perspective, public-private partnerships, green bonds, and climate funds are multiplying. ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) metrics are driving institutional investors to shift portfolios toward sustainable infrastructure. Nations that prioritize energy innovation are positioning themselves for leadership in the coming global energy economy.
Practical Insights for Stakeholders
To maximize gains, governments must streamline permitting processes, improve grid infrastructure, and support research and workforce development. Businesses need to integrate renewable solutions into operations, from green supply chains to net-zero buildings.
Policymakers, investors, and entrepreneurs alike must recognize that the future of renewable energy is not just about avoiding climate disaster—it’s about securing economic stability, national security, and environmental health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the projected share of solar energy by 2030? Solar is expected to become the world’s largest source of renewable electricity by 2029.
How much investment is going into clean energy in 2025? An estimated USD 2.2 trillion is projected, outpacing fossil fuel investments.
Which innovations are most impactful? Floating wind turbines, perovskite solar panels, hydrogen fuel cells, and smart grids.
What governments are leading this transition? The US, EU, China, Australia, and India are at the forefront of renewable energy policies.
What economic benefits are expected? Massive job creation, reduced energy costs, and strong investment returns.
How does renewable energy help the environment? It reduces emissions, air pollution, and fossil fuel dependence while conserving water.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of renewable energy is both promising and necessary. Innovations in solar, wind, hydro, bioenergy, and storage are making clean energy more reliable and scalable. Governments and investors are stepping up. Environmental and economic gains are aligning. As we look toward 2030 and beyond, the global transition to renewables is not only inevitable—it’s accelerating.


